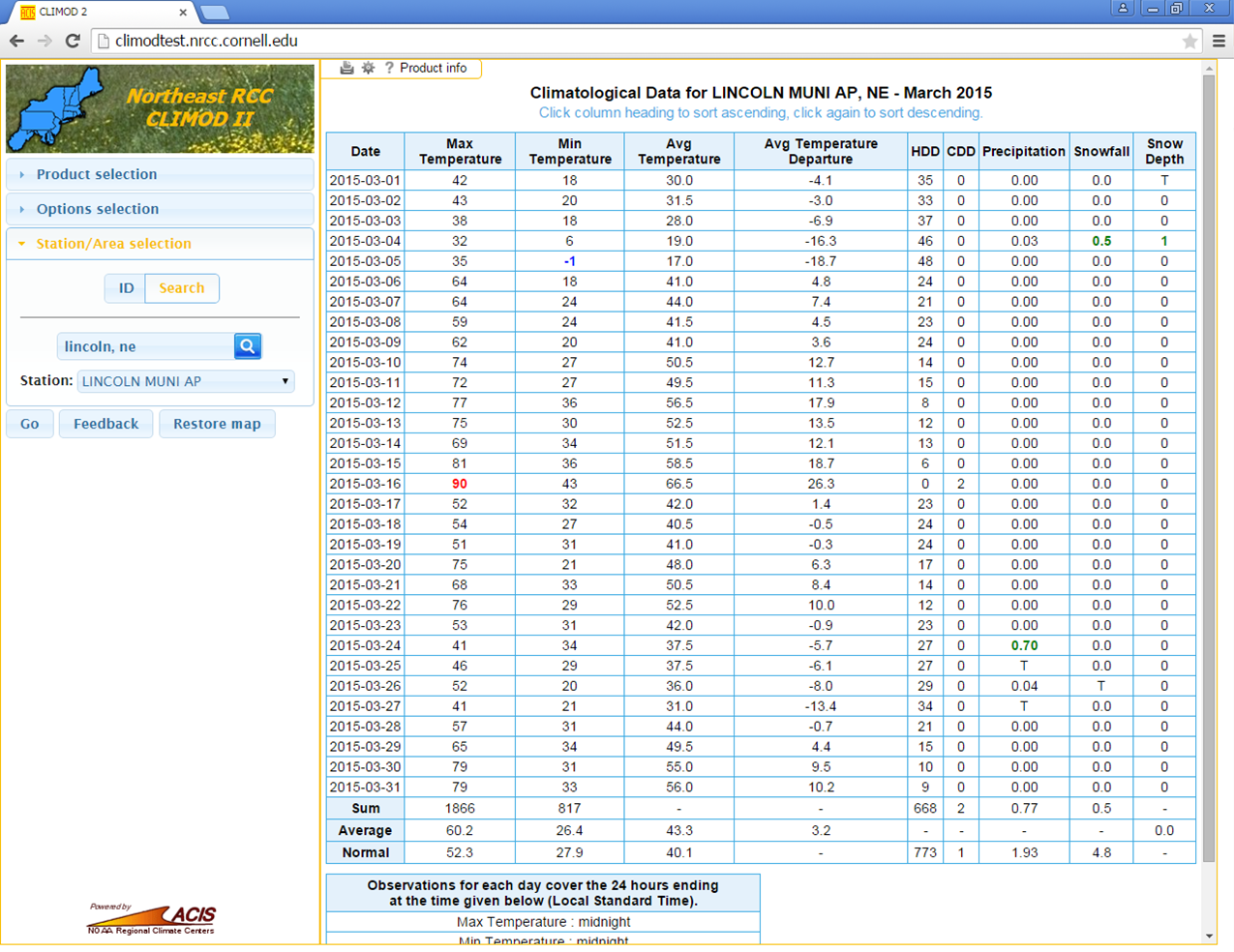
CLIMOD - Climate Information for Management and Operational Decisions
The CLimate Information for Management and Operational Decisions (CLIMOD) system provides clients with web access to a vast amount of data and information in the ACIS database. Some examples of products available through the CLIMOD system include: daily temperature and precipitation observations, normals and records for several thousand sites around the country and monthly data summaries. Additional derived products, such as growing, heating and cooling degree day accumulations, that are useful for planning and managing climate-sensitive operations, are also available through the CLIMOD system. The CLIMOD system is geared toward users who need climate data on an ongoing monthly or daily basis. Users who have a one-time or infrequent need for weather or climate data should contact the HPRCC directly. CLIMOD access is only available on a subscription basis.
Website: http://climod2.nrcc.cornell.edu/

Classic Online Services
The High Plains Regional Climate Center (HPRCC) Classic Online Services computer system allows users access to the entire AWDN data set, as well as the National Weather Service Cooperative Weather Network. HPRCC's AWDN records hourly data for air temperature and humidity, soil temperature, wind speed and direction, solar radiation, and precipitation. This system has been designed primarily for those who need to access the data on a regular basis and would like to retrieve the data manually from their own computer. HPRCC Classic Online Services is a fee-based data retrieval system. However, you may request time on the system be granted to you if the account is to be used only for classroom use or you are a High Plains Regional Climate Center cooperator.
Source: the High Plains Regional Climate Center (HPRCC)
UV-B Monitoring Climatological and Research Network
The UVMRP was tasked to provide information on the geographical distribution and temporal trends of UV-B (ultraviolet -B) radiation in the United States, as this information is critical to the assessment of the potential impacts of increasing ultraviolet radiation levels on agricultural crops and forests. Specifically the monitoring program:
- Provides information to the agricultural community and others about the climatological and geographical distribution of UV-B irradiance;
- Furnishes the basic information necessary to support evaluations of the potential damaging effects of UV-B to agricultural crops and forests;
- Supplies ground truth for satellite measurements of UV-B, and basic information for radiation transfer model calculations;
- Establishes long-term records of UV-B irradiance necessary to assess trends. The program consists of both a research component and a climatologic network.
The station near Mead, NE has been collecting data since May 1996.
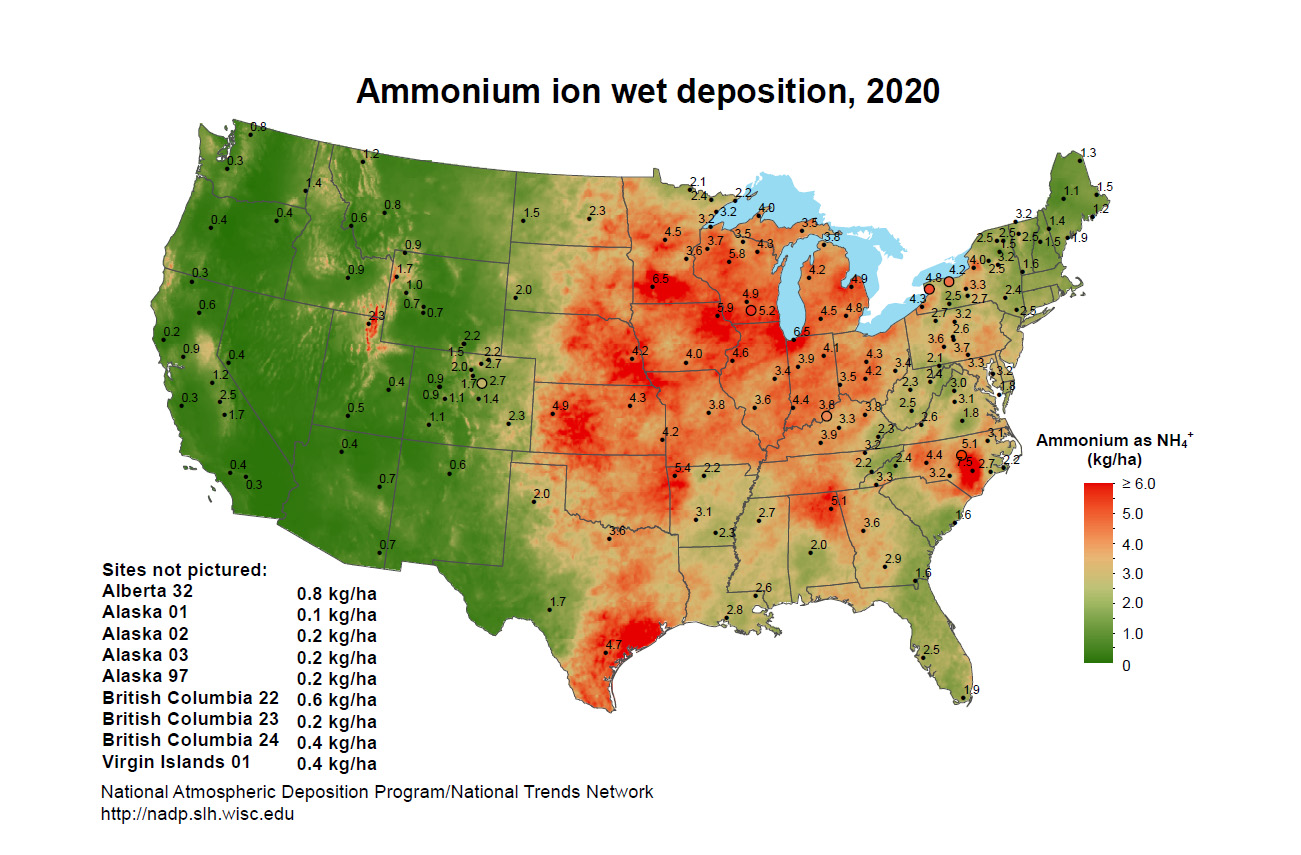
National Atmospheric Deposition Program
In 1977, U.S. State Agricultural Experiment Stations (SAES) organized a project, later titled the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP), to measure atmospheric deposition and study its effects on the environment.
Sites in the NADP precipitation chemistry network began operations in 1978 with the goal of providing data on the amounts, trends, and geographic distributions of acids, nutrients, and base cations in precipitation. The network grew rapidly in the early 1980s. The network name was changed to NADP National Trends Network (NTN). Today, the NADP is SAES National Research Support Project - 3. The NTN network currently has 250 sites. The Site near Mead, NE began collecting data in July 1978.
A second network, the Atmospheric Integrated Research Monitoring Network (AIRMoN) joined the NADP in 1992, and currently has seven sites. Although measuring the same chemicals as NTN, AIRMoN sampling is daily rather than weekly. These higher resolution samples enhance researchers' ability to evaluate how emissions affect precipitation chemistry using computer simulations of atmospheric transport and pollutant removal. This network also evaluates alternative sample collection and preservation methods.
A third network, the Mercury Deposition Network (MDN) joined the NADP in 1996, and currently has over 100 sites in the United States and Canada. All MDN samples are analyzed for total mercury, and some for the more toxic methyl mercury. Fish consumption advisories for mercury exist in almost every state in the country warning people to limit consumption of fish, and a few states also have wildlife consumption advisories for mercury. Researchers use MDN data to evaluate the role of precipitation as a source of mercury in these water bodies. Site site near Mead, NE began collection data in June 2007.
Website: http://nadp.slh.wisc.edu/